Thursday, December 13, 2012
C++ TUTORIAL FOR BEGINNERS: Variables and their practical applications in calculations
What are C++ variables?
Variables are simply values that change as opposed to constants which do not change.
To illustrate the usefulness of variables, let us use them in an example to calculate the net profit of a video game store.
Given:
On a certain week, a video game store has a total sales of $9000 and total expenses of $6000. On the following week, total sales rose to $9500 while the total expenses increased to $6500. Calculate the net profit of the video game store on those two weeks.
Objective: How to calculate the net profit of a given video game store
Directive: #include <iostream>
Namespace: std
Function: main
Variables: sales, expenses, profit
Data types of variables: int (integer)
Statements: cout, return
Output:
Net profit = 6000
C++ source code:
/*
PROGRAM 2: Calculation of net profit of a video game store
AUTHOR: eternaltreasures
DATE: 2010 August 26
*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int sales, expenses, profit;
//First week:
sales = 9000;
expenses = 6000;
//Second week:
sales = sales + 9500;
expenses = expenses + 6500;
//Net profit of the video game store:
profit = sales - expenses;
cout << "Net profit = ";
cout << profit;
return 0;
}
Notes:
* During the first week, initial value of the variable sales is 9000 and the variable expenses is 6000.
* On the second week, the value of the variable sales is 9000 + 9500 = 18500.
* Also on the second week, the value of the variable expenses is 6000 + 6500 = 12500.
* Variables change values depending on the operations done to them on the program.
C++ String Manipulation functions: Card Verification System - Examples of String append & Substring, Reading database file
/*
PROGRAM: String Manipulation functions - Examples of String append and Substring
PURPOSE: The user is prompted to input a card number with 16 digits (four numbers
at a time, starting from digits one to four), then the program uses the
string append function to connect these series of four numbers to make
up a string of 16 numbers. This card number is then matched against a
card database file using the substring function to extract the first 16
characters within the record then compared to the user input. If a match
is found, the program returns a message "Card verification successful!",
otherwise, it will display a "Card not found on database" message on the
screen.
LANGUAGE: C++
AUTHOR: eternaltreasures
DATE: 2010 October 3
*/
#include<iostream>
#include <string>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
#define newline '\n'
string card_database_record;
string card_database_record_substring;
string string4;
string card_input_record;
bool cardfound = false;
int database_record_index = 0;
void input_card_number ()
{
cout << newline;
cout << "Welcome to the Secure Card Verification System!";
cout << newline;
cout << newline;
cout << "Enter your 16-digit card number:";
cout << newline;
cout << newline;
cout << "1st to 4th digit: "; cin >> string4;
card_input_record.append (string4);
database_record_index = database_record_index + 4;
cout << "5th to 8th digit: "; cin >> string4;
card_input_record.append (string4);
database_record_index = database_record_index + 4;
cout << "9th to 12th digit: "; cin >> string4;
card_input_record.append (string4);
database_record_index = database_record_index + 4;
cout << "13th to 16th digit: "; cin >> string4;
card_input_record.append (string4);
database_record_index = database_record_index + 4;
}
void compare_match_input ()
{
card_database_record_substring = card_database_record.substr (0, database_record_index);
if (card_input_record == card_database_record_substring)
{
cout << "Card " << card_input_record << ": Card verification successful!";
cardfound = true;}
}
void read_database_file ()
{
ifstream card_database_file;
card_database_file.open ("database.txt");
if (card_database_file.is_open())
{
while (!card_database_file.eof())
{
card_database_file >> card_database_record;
cout << endl;
compare_match_input ();
if (cardfound = false)
cout << "End of file: Card not found on database.";
}
}
else
{ cout << "Input file not successfully opened.";
card_database_file.close();
}
}
int main()
{
input_card_number ();
read_database_file ();
return 0;
}
C++ TUTORIAL FOR BEGINNERS: How to generate a random number, maximum random number & random numbers within a given range
/*
PROGRAM: How to generate a random number, maximum random number and random numbers within a given range
PURPOSE:
The user is prompted to press any key to begin generating a random number. The program
then returns to display a random number then the Maximum random number is displayed.
The second part of the program is to let the user put a higher limit for the random
numbers and a lower limit to generate random numbers within the required range of values.
The program shows the values of those random numbers in the specified given range of limits.
LANGUAGE: C++
AUTHOR: eternaltreasures
DATE: 2010 October 6
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
int random_number;
char random_number_obtain;
int random_number_generator ()
{
/* srand (time(0)) initializes the random number generator. Each time you run the program, time(0) will
capture the integer value of the Seconds from the system clock and will be used by the random number
generator as a starting value number called the SEED.
RAND_MAX returns the value of the maximum random number that could be generated and is compiler
dependent but it usually equal to 32767.
*/
srand(time(0));
int maximum_random_number;
cout << endl;
cout << "Random Number Generator" << endl << endl;
cout << "Press Any key to generate a random number."; cin >> random_number_obtain;
random_number = rand ();
maximum_random_number = RAND_MAX;
cout << endl;
cout << "Random number generated is: " << random_number << endl << endl;
cout << "MAXIMUM RANDOM NUMBER: " << maximum_random_number << endl << endl;
}
int random_number_generator_within_range ()
{
int random_counter;
int random_number_high;
int random_number_low;
int random_number_range;
cout << endl;
cout << "Random Number Generator within a given Range" << endl << endl;
cout << "Enter the random number higher limit: "; cin >> random_number_high;
cout << "Enter the random number lower limit: "; cin >> random_number_low;
random_number_range = (random_number_high - random_number_low) + 1;
for (random_counter = 0; random_counter < random_number_high; random_counter ++)
{
random_number = random_number_low + int(random_number_range * rand()/(RAND_MAX + 1));
cout << random_number << endl;
}
}
int main ()
{
bool random_number_generate = true;
random_number_generator ();
random_number_generator_within_range ();
random_number_generator ();
}
C++ TUTORIAL FOR BEGINNERS: How to determine a given number if it is Odd or Even number
/*
PROGRAM: How to determine a given number if it is Odd or Even number
PURPOSE:
In order to know whether a number is even or odd, we must use the concept
of the Modulo Operation (mod). The modulo operation will compute the Remainder of
dividing a given number by another number. For example, if we divide 10 by 2, the
quotient or result is 5 and the remainder is 0. Therefore 10 mod 2 is 0.
On the other hand, if we divide 11 by 2, the quotient or result is 5
Remainder 1. In this case 11 mod 2 is 1.
In our C++ program, we will use the Integer modulo operator % to determine
if a number input by a user is an odd or even number.
LANGUAGE: C++
AUTHOR: eternaltreasures
DATE: 2010 October 6
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
void modulo_odd_even ()
{
int input_number;
cout << endl;
cout << "Determination of Odd or Even Numbers" << endl << endl;
cout << "Please enter any number: "; cin >> input_number;
//input_nmuber % 2 will find the remainder of input_number divided by 2.
//If the remainder is 0, then the number is even, otherwise it is odd.
if (input_number % 2 == 0)
cout << input_number << " is an Even Number" << endl << endl;
else
cout << input_number << " is an Odd Number" << endl << endl;
}
int main()
{
bool endless_loop = true;
//for loop code leading to an ENDLESS LOOP (online mode)
//for loop without increment
for (endless_loop; (endless_loop != false);)
modulo_odd_even ();
}
C++ Database Name Search Program: User inputs last, first name, search from a name file, match using string function
/*
PROGRAM: Database Name Search
PURPOSE: Last name and first name input are compared to the records on a namefile.
If a match is found, then display "Record found at database".
NOTE: string.find is used here (which is not the best method) just to show
an example of its use. I know that experienced C++ database programmers have
their best and most recommended ways for a name search program, you are
welcome to comment and to share your code (thanks in advance).
LANGUAGE: C++
AUTHOR: eternaltreasures
DATE: 2010 October 2
*/
// reading a text file
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
#define newline '\n'
string recordline;
string last_name_input;
string first_name_input;
int recordnumber = 0;
bool namefound = false;
ifstream recordfile ("namefile.txt");
//Welcome introduction
void welcome_introduction ()
{
cout << newline;
cout << "Welcome to the Records Database Facility!";
cout << newline;
cout << newline;
cout << "Enter name to search: ";
cout << newline;
cout << newline;
cout << "Last name: "; cin >> last_name_input;
cout << "First name: "; cin >> first_name_input;
cout << newline;
}
//Compare the user input last name and first name against the database record file
void stringmatch ()
{
//location1 and location2 are variables to receive the user's last name and first name
string::size_type location1 = recordline.find(last_name_input, 0);
string::size_type location2 = recordline.find(first_name_input, 0);
if (location1 != string::npos)
{
if (location2 != string::npos)
{
cout << "Name found at database: ";
cout << "Record " << recordnumber << " " << recordline;
namefound = true;
cout << newline;
}
}
}
//Read the Name Database file
//Check the last name and first name inputs if found on the file (database)
void read_record_file ()
{
if (recordfile.is_open())
{
while (!recordfile.eof() )
{
getline (recordfile, recordline);
recordnumber = recordnumber + 1;
stringmatch ();
}
if (recordfile.eof())
{
if (namefound == false)
cout << "eof: Record not found on database.";
}
}
else
{
cout << "Error opening the file";
recordfile.close();
}
}
int main ()
{
welcome_introduction ();
read_record_file ();
return 0;
}
C++ TUTORIAL FOR BEGINNERS: How to display characters on the screen
Objective: Displaying characters on the screen
Directive: #include <iostream>
Namespace: std
Function: main
Statements: cout, return
Output:
This is a simple C++ program.
It will display these characters on the screen.
C++ source code:
/*
PROGRAM 1: Displaying characters on the screen
AUTHOR: eternaltreasures
DATE: 2010 August 25
*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
cout << "This is a simple C++ program.\n";
cout << "It will display these characters on the screen.";
return 0;
}
// End of the program.
Explanations:
/*
Block of comments about the program, author, date...
*/
#include <iostream>
Preprocessor command to include the iostream file to be used for input-output operations.
using namespace std;
The contents of the namespace called std would be used. A namespace is a "container" for elements of standard C++ library.
semicolon ;
A semicolon separates statements.
int main ()
This is where the program begins to execute.
braces { }
The main function executes anything that is enclosed within these braces.
cout << "This is a simple C++ program.\n";
The cout is a statement for displaying on the screen the characters within the quotes "".
\n is for starting a new line.
return 0;
The return statement ends the execution of the main function.
0 return code means the execution is OK.
// End of the program.
A single line of comment uses two forward slashes.
Sunday, December 9, 2012
Useful US Equivalent Measurement Units, Approximates, Estimates, and Rough Conversions
HOME:
- cooking in the kitchen
- medicine cabinet in the bathroom
- medications and prescription drugs
- food and drink measurements
- home hobbies
- home work and assignments
- and more...
SCHOOL:
- school projects
- physics subject
- chemistry subject
- mathematics subject
- practical arts and trades subjects
- and more...
BUSINESS/COMMERCIAL:
- drugstores and pharmacies
- canteen, cafeteria, coffee shops, restaurants
- groceries and supermarkets
- shopping centres
- home hardware stores
- factories and warehouses
- manufacturing plants
- and more...
---------------------------------------------------
Note:
The symbol ~ has been used here to mean approximate.
ONE CENTIMETER (cm):
1 cm ~ 0.4 inch
1 cm ~ 2/5 inch
ONE INCH:
1 inch ~ 2 1/2 centimeters
1 inch ~ 2.5 centimetres
ADULT HUMAN BODY PARTS MEASUREMENT APPROXIMATIONS:
nail width of little finger ~ 1 centimeter
1 thumb width ~ 1 inch
1 little finger length ~ 2 inches
1 index finger length ~ 3 inches
1 palm width ~ 4 inches
from index finger to front edge of thumb ~ 5 inches
from index finger to back edge of thumb ~ 6 inches
from middle finger to back edge of thumb ~ 7 inches
from middle finger to the wrist joint ~ 8 inches
1 human foot ~ 12 inches
1 cubit (middle finger to elbow) ~ 1 1/2 foot
1 cubit (middle finger to elbow) ~ 18 inches
1 step at normal walking pace ~ 2 feet
1 step at normal walking pace ~ 24 inches
1 arm length ~ 2 1/2 feet
1 arm length ~ 30 inches
ONE GRAM:
1 gram of water = 1 cubic centimeter (cc) of water
1 gram of water = 1 ml of water
ONE MILLILITER (ml or mL):
1 ml = 1 cc (cubic centimeter)
1 ml = 16 drops
ONE TEASPOON:
1 teaspoon ˜ 5 mL
ONE TABLESPOON:
1 tablespoon ~ 3 teaspoons
1 tablespoon ˜ 15 mL
ONE FLUID OUNCE:
1 US fluid ounce = 2 tablespoons
1 US fluid ounce = 6 teaspoons
1 US fluid ounce ~ 30 ml
ONE GILL:
1 US gill = 1/2 cup
1 US gill = 4 US fluid ounces
1 US gill = 8 tablespoons
ONE CUP:
1 cup = 16 tablespoons
1 cup ˜ 250 mL
CAN OF SODA, COLA, POP, SOFTDRINK:
1 can of soda pop softdrink ~ 1 1/2 cups
1 can of soda pop softdrink = 355 ml
ONE PINT:
1 pint = 2 cups
BOTTLED WATER:
1 bottled water 500 ml = 1/2 liter
1 bottled water 500 ml ~ 2 cups
GLASS OF WATER:
1 small glass of water ~ 1 pint
1 small glass of water ~ 2 cups
1 big glass of water ~ 2 1/2 cups
ONE QUART:
1 quart ~ 1 liter
1 quart = 2 pints
1 quart = 4 cups
ONE LITER:
1 liter ~ 1 quart
1 liter ~ 2 pints
1 liter ~ 4 cups
1 liter of water = 1 kilogram (kg.)
1 liter of water ~ 2 pounds (lbs.)
ONE GALLON:
1 gallon ~ 4 liter
1 gallon = 4 quarts
1 gallon = 8 pints
1 gallon = 16 cups
1 gallon = 32 gills
ONE PECK:
1 peck ~ 2.3 gallons liquid measure
1 peck = 2 gallons dry measure
ONE DRINKING WATER DISPENSER BOTTLE:
1 commercial drinking water dispenser bottle = 5 gallons
1 commercial drinking water dispenser bottle ~ 19 liters
ONE BUCKET:
1 bucket = 5 gallons liquid measure
1 bucket ~ 4 gallons dry measure
ONE BUSHEL:
1 bushel ~ 9 gallons liquid measure
1 bushel = 8 gallons dry measure
ONE KEG:
1 keg (beer) = 1/2 beer barrel
1 keg (beer) = 15.5 U.S. gallon
ONE BARREL:
1 barrel = 31.5 gallons (liquid measure)
1 barrel = 27 gallons (dry measure)
1 U.S. beer barrel = 31 U.S. gallons
1 oil barrel = 42 US gallons
1 barrel (wine) = 38 gallons (liquid measure)
1 barrel (wine) = 32.5 gallons (dry measure)
ONE DRUM (petroleum):
1 drum = 55 gallons liquid measure
1 drum = 47 gallons dry measure
ONE PIPE:
1 pipe ~ 2 drums (petroleum)
1 pipe = 3 barrels (petroleum)
1 pipe = 126 gallons (liquid measure)
PICTURES:
 |
| A 5 gallon water dispenser bottle. |
 |
| A 355 ml canned softdrink approximately 1 and half cup. |
 |
| A 500 ml bottled water is about 2 cups. |
 |
| A 710 ml pop softdrink or carbonated beverage. |
 |
| A big glass is about 2 and half cups. |
 |
| A cup is 250 ml approximately. |
 |
| A gallon is equal to 4 quarts (approximately 4 liters). |
 |
| A pint of ice cream is equal to 2 cups. |
 |
| A quart of ice cream is equal to 2 pints or 4 cups. |
 |
| A small glass is about 2 cups. |
 |
| One cup is equal to 16 tablespoons. |
..png) |
| One liter of vinegar is equal to 4 cups (estimate). |
 |
| One tablespoon is roughly equal to 15 mL. |
 |
| One teaspoon is roughly equal to 5 mL. |
 |
| One US fluid ounce is equal to 2 tablespoons and approximately 30 ml. |
 |
| The cubit or length from the middle finger to the elbow is close to 18 inches. |
 |
| The distance from the tip of the index finger to the front edge of the thumb is 5 inches approx. |
 |
| The distance from the tip of the middle finger to the wrist joint is 8 inches approximately. |
 |
| The human foot is approximately 12 inches. |
 |
| The index finger is about 3 inches long. |
 |
| The little finger has a length of about 2.5 inches. |
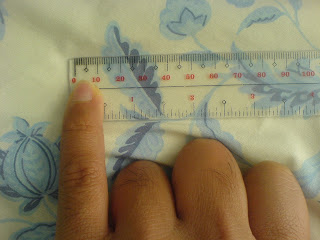 |
| The nail width of the little finger is 1 cm approx. |
 |
| The palm width is about 4 inches wide. |
 |
| The width of the thumb is about 1 inch wide. |
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)